
FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
m (Bot: Automated text replacement (-\#\* +#)) |
m (Bot: Automated text replacement (-#<br>\n +)) |
||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
Did Sidney Rigdon give public approval to the Danites during a speech he delivered on June 17, 1838? | Did Sidney Rigdon give public approval to the Danites during a speech he delivered on June 17, 1838? | ||
|authorsources=<br> | |authorsources=<br> | ||
*Winn, 124. | *Winn, 124. | ||
*Reed Peck, ''Reed Peck Manuscript'', 3. | *Reed Peck, ''Reed Peck Manuscript'', 3. | ||
| Claims made in "Chapter 7: Woe In Ohio" | A FAIR Analysis of: One Nation Under Gods, a work by author: Richard Abanes
|
Claims made in "Chapter 9: March to Martyrdom" |
| Claim Evaluation |
| One Nation Under Gods |
|
Jump to details:
The author claims that "Twenty-first century Mormonism" promotes the idea that Cain, Abel, Jared, Enoch, Methuselah, and Noah lived in Missouri.
Author's sources:
- No source provided.
Did Oliver Cowdery accuse Joseph of having a "dirty, nasty, filthy affair" with Fanny Alger?
Author's sources:
- Oliver Cowdery, letter to Warren Cowdery, January 21, 1838.
One of the wives about whom we know relatively little is Fanny Alger, Joseph's first plural wife, whom he came to know in early 1833 when she stayed at the Smith home as a house-assistant of sorts to Emma (such work was common for young women at the time). There are no first-hand accounts of their relationship (from Joseph or Fanny), nor are there second-hand accounts (from Emma or Fanny's family). All that we do have is third hand (and mostly hostile) accounts, most of them recorded many years after the events.
Unfortunately, this lack of reliable and extensive historical detail leaves much room for critics to claim that Joseph Smith had an affair with Fanny and then later invented plural marriage as way to justify his actions which, again, rests on dubious historical grounds. The problem is we don't know the details of the relationship or exactly of what it consisted, and so are left to assume that Joseph acted honorably (as believers) or dishonorably (as critics).
There is some historical evidence that Joseph Smith knew as early as 1831 that plural marriage would be restored, so it is perfectly legitimate to argue that Joseph's relationship with Fanny Alger was such a case. Mosiah Hancock (a Mormon) reported a wedding ceremony; and apostate Mormons Ann Eliza Webb Young and her father Chauncery both referred to Fanny's relationship as a "sealing." Ann Eliza also reported that Fanny's family was very proud of Fanny's relationship with Joseph, which makes little sense if it was simply a tawdry affair. Those closest to them saw the marriage as exactly that—a marriage.
Joseph Smith came to know Fanny Alger in early 1833 when she stayed at the Smith home as a house-assistant to Emma. Neither Joseph nor Fanny ever left any first-hand accounts of their relationship. There are no second-hand accounts from Emma or Fanny's family. All that we do have is third hand accounts from people who did not directly observe the events associated with this first plural marriage, and most of them recorded many years after the events.
Benjamin F. Johnson stated that in 1835 he had "learned from my sister’s husband, Lyman R. Sherman, who was close to the Prophet, and received it from him, 'that the ancient order of Plural Marriage was again to be practiced by the Church.' This, at the time did not impress my mind deeply, although there lived then with his family (the Prophet’s) a neighbor’s daughter, Fannie Alger, a very nice and comely young woman about my own age, toward whom not only myself, but every one, seemed partial, for the amiability for her character; and it was whispered even then that Joseph loved her."[1]
Mosiah Hancock discusses the manner in which the proposal was extended to Fanny, and states that a marriage ceremony was performed. Joseph asked Levi Hancock, the brother-in-law of Samuel Alger, Fanny’s father, to request Fanny as his plural wife:
Samuel, the Prophet Joseph loves your daughter Fanny and wishes her for a wife. What say you?" Uncle Sam says, "Go and talk to the old woman [Fanny’s mother] about it. Twill be as she says." Father goes to his sister and said, "Clarissy, Brother Joseph the Prophet of the most high God loves Fanny and wishes her for a wife. What say you?" Said she, "Go and talk to Fanny. It will be all right with me." Father goes to Fanny and said, "Fanny, Brother Joseph the Prophet loves you and wishes you for a wife. Will you be his wife?" "I will Levi," said she. Father takes Fanny to Joseph and said, "Brother Joseph I have been successful in my mission." Father gave her to Joseph, repeating the ceremony as Joseph repeated to him.[2]
There is historical evidence that Joseph Smith knew as early as 1831 that plural marriage would be restored. Mosiah Hancock (a Mormon) reported a wedding ceremony in Kirtland, Ohio in 1833.
Apostate Mormons Ann Eliza Webb Young and her father Chauncery both referred to Fanny's relationship as a "sealing." Ann Eliza also reported that Fanny's family was very proud of Fanny's relationship with Joseph, which makes little sense if it was simply a tawdry affair. Those closest to them saw the marriage as exactly that—a marriage.
Some have wondered how the first plural marriages (such as the Alger marriage) could have occurred before the 1836 restoration of the sealing keys in the Kirtland temple (see D&C 110). This confusion occurs because we tend to conflate several ideas. They were not all initially wrapped together in one doctrine:
Thus, the marriage to Fanny would have occurred under the understanding #1 above. The concept of sealing beyond the grave came later. Therefore, the marriage of Joseph and Fanny would have been a plural marriage, but it would not have been a marriage for eternity.
Perhaps it is worth mentioning that priesthood power already gave the ability to ratify certain ordinances as binding on heaven and earth (D&C 1:8), that the sealing power was given mention in earlier revelations such as Helaman 10:7, and that the coming of Elijah and his turning of the hearts of children and fathers was prophesied in 3 Nephi 25:5-6. This supports the view that it is unlikely that Joseph was just making up the sealing power and priesthood power extemporaneously to justify getting married to Fanny and having sexual relations with her.
Some of Joseph's associates, most notably Oliver Cowdery, perceived Joseph's association with Fanny as an affair rather than a plural marriage. Oliver, in a letter to his brother Warren, asserted that "in every instance I did not fail to affirm that which I had said was strictly true. A dirty, nasty, filthy affair of his and Fanny Alger's was talked over in which I strictly declared that I had never deserted from the truth in the matter, and as I supposed was admitted by himself."[3]
Gary J. Bergera, an advocate of the "affair" theory, wrote:
I do not believe that Fanny Alger, whom [Todd] Compton counts as Smith’s first plural wife, satisfies the criteria to be considered a "wife." Briefly, the sources for such a "marriage" are all retrospective and presented from a point of view favoring plural marriage, rather than, say, an extramarital liaison…Smith’s doctrine of eternal marriage was not formulated until after 1839–40. [4]
There are several problems with this analysis. While it is true that sources on Fanny are all retrospective, the same is true of many early plural marriages. Fanny's marriage has more evidence than some. Bergera says that all the sources about Fanny's marriage come "from a point of view favoring plural marriage," but this claim is clearly false.
For example, Fanny's marriage was mentioned by Ann Eliza Webb Young, a later wife of Brigham Young's who divorced him, published an anti-Mormon book, and spent much of her time giving anti-Mormon, anti-polygamy lectures. Fanny stayed with Ann Eliza's family after leaving Joseph and Emma's house, and both Ann Eliza and her father Chauncey Webb [5] refer to Joseph's relationship to Fanny as a "sealing." [6] Eliza also noted that the Alger family "considered it the highest honor to have their daughter adopted into the prophet's family, and her mother has always claimed that she [Fanny] was sealed to Joseph at that time." [7] This would be a strange attitude to take if their relationship was a mere affair. And, the hostile Webbs had no reason to invent a "sealing" idea if they could have made Fanny into a mere case of adultery.
It seems clear, then, that Joseph, Fanny's family, Levi Hancock, and even hostile witnesses saw their relationship as a marriage, albeit an unorthodox one. The witness of Chauncey Webb and Ann Eliza Webb Young make it untenable to claim that only a later Mormon whitewash turned an affair into a marriage.
It appears that shortly after the April 3 vision, Joseph Smith recorded a first-hand account of the vision in his own personal journal or notes. That original record has not been found and is probably lost. Nonetheless, these important visitations were documented in other contemporaneous records. Within a few days, the Prophet’s secretary Warren Cowdery transcribed Joseph’s first-hand account into a third-hand account to be used in the Church history then being composed. |
|
Despite the importance of Elijah and the Kirtland Temple visitations, Joseph Smith did not publicly teach eternal marriage for perhaps six years after he received the authority to perform those ordinances. |
|
Sometime in late 1835 or early 1836, in a priesthood ceremony performed by Levi Hancock, Joseph secretly married Fanny Alger, a domestic living in the Smith home. When Oliver Cowdery and Emma Smith learned of the relationship, they did not consider it a legitimate marriage. Joseph was unable to convince them the polygamous marriage was approved of God. Fanny left the area and married a non-member a few months later and never returned to the Church. Her family and other who were close to her remained true to Joseph Smith, following him to Nauvoo and later migrating with the Saints to Utah. |
Critical sources |
|
In 1872, William McLellin (then an apostate excommunicated nearly 34 years prior) wrote a letter to Emma and Joseph's son, Joseph Smith III:
Now Joseph I will relate to you some history, and refer you to your own dear Mother for the truth. You will probably remember that I visited your Mother and family in 1847, and held a lengthy conversation with her, retired in the Mansion House in Nauvoo. I did not ask her to tell, but I told her some stories I had heard. And she told me whether I was properly informed. Dr. F. G. Williams practiced with me in Clay Co. Mo. during the latter part of 1838. And he told me that at your birth your father committed an act with a Miss Hill [sic]—a hired girl. Emma saw him, and spoke to him. He desisted, but Mrs. Smith refused to be satisfied. He called in Dr. Williams, O. Cowdery, and S. Rigdon to reconcile Emma. But she told them just as the circumstances took place. He found he was caught. He confessed humbly, and begged forgiveness. Emma and all forgave him. She told me this story was true!! Again I told her I heard that one night she missed Joseph and Fanny Alger. She went to the barn and saw him and Fanny in the barn together alone. She looked through a crack and saw the transaction!!! She told me this story too was verily true. [8]
Some critics interpret "transaction" to mean intercourse in this case and that Emma caught Joseph in the very act. But McLellin reported on the event again three years afterwards in 1875 to J. H. Beadle and makes it clear that he is talking about the wedding or sealing ceremony:
He [McLellin] was in the vicinity during all the Mormon troubles in Northern Missouri, and grieved heavily over the suffering of his former brethren. He also informed me of the spot where the first well authenticated case of polygamy took place in which Joseph Smith was "sealed" to the hired girl. The "sealing" took place in a barn on the hay mow, and was witnessed by Mrs. Smith through a crack in the door! The Doctor was so distressed about this case, (it created some scandal at the time among the Saints,) that long afterwards when he visited Mrs. Emma Smith at Nauvoo, he charged her as she hoped for salvation to tell him the truth about it. And she then and there declared on her honor that it was a fact—"saw it with her own eyes." [9]
Ann Eliza Webb, who was born in 1844, was not even alive at the time of these events, could only only comment based upon what her father told her about Joseph and Fanny. Ann apostatized from the Church and wrote an "expose" called Wife No. 19, or The story of a Life in Bondage. She described Fanny as follows:
Mrs. Smith had an adopted daughter, a very pretty, pleasing young girl, about seventeen years old. She was extremely fond of her; no mother could be more devoted, and their affection for each other was a constant object of remark, so absorbing and genuine did it seem. Consequently is was with a shocked surprise that people heard that sister Emma had turned Fanny out of the house in the night.[10]
The first mention of a pregnancy for Fanny is in an 1886 anti-Mormon work, citing Chauncey Webb, with whom Fanny reportedly lived after leaving the Smith home.[11] Webb claimed that Emma "drove" Fanny from the house because she "was unable to conceal the consequences of her celestial relation with the prophet." If Fanny was pregnant, it is curious that no one else remarked upon it at the time, though it is possible that the close quarters of a nineteenth-century household provided Emma with clues. If Fanny was pregnant by Joseph, the child never went to term, died young, or was raised under a different name.
Fawn Brodie, in her critical work No Man Knows My History: The Life of Joseph Smith, claimed that "there is some evidence that Fannie Alger bore Joseph a child in Kirtland."[12] However, DNA research in 2005 confirmed Fanny Alger’s son Orrison Smith is not the son of Joseph Smith, Jr.[13]
Did Joseph allow the formation of the Danites?
Author's sources:
- Hill 75.
- William Edwin Berrett, The Restored Church, 198.
- Sampson Avard, Correspondence, Orders, 97-98.
- Winn, 123.
- David Whitmer, An Address to All Believers in Christ, 27-28.
The Danites were a brotherhood of church members that formed in Far West, Missouri in mid-1838. By this point in time, the Saints had experienced serious persecution, having been driven out of Kirtland by apostates, and driven out of Jackson County by mobs. Sidney Rigdon was publicly preaching that the Saints would not tolerate any more persecution, and that both apostates and mobs would be put on notice. The Danite organization took root within this highly charged and defensive environment.
The Danites are sometimes confused with the “Armies of Israel,” which was the official defensive organization that was tasked with defending the Saints, and which was supported by Joseph Smith and Sidney Rigdon. This is complicated by the fact that members of the Danite organization also served in the “Armies of Israel.”
Regardless of their original motives, the Danites ultimately were led astray by their leader, Sampson Avard. Avard attempted to blame Joseph Smith in order to save himself. Joseph, however, clearly repudiated both the organization and Avard.
Did Sidney Rigdon give public approval to the Danites during a speech he delivered on June 17, 1838?
Author's sources:
- Winn, 124.
- Reed Peck, Reed Peck Manuscript, 3.
Rigdon's speech was directly targeted at dissenters within the Church, and strongly implied that they should leave.
Leland H. Gentry,
The first official encouragement given to removing these "dissenters" from Caldwell County came in the form of a speech given by Sidney Rigdon on Sunday, 17 June 1838. Familiarly known in church history annals as the "Salt Sermon," Rigdon's address remains one of the controversial events of the period.[1]:423
Gentry notes John Corrill's description of the sermon,
President Rigdon delivered from the pulpit what I call the "Salt Sermon;" 'If the salt hath lost its savour, it is thenceforth good for nothing but to be cast out and trodden under the feet of men,' was his text; and although he did not call names in his sermon, yet it was plainly understood that he meant the dissenters or those who had denied the faith. He indirectly accused some of them with crime.[2]
The Danites were led by Dr. Sampson Avard, and the group appears to have been formally formed about the time that Sidney Rigdon gave his “Salt Sermon” in Far West, in which he gave apostates an ultimatum to get out or suffer consequences.[1]:4 According to Avard, the original purpose of the band was to “drive from the county of Caldwell all that dissented from the Mormon church.”[3]:25 Once the dissenters had left the country, the Danites turned their attention to defending the Saints from mobs.
Author's quote: "Such historical revisionism is typical of Mormon historians, who must at all costs, preserve the integrity of early Mormon leaders."
Author's sources:
- Author's opinion.
The author is expressing his negative opinion as if it were fact.
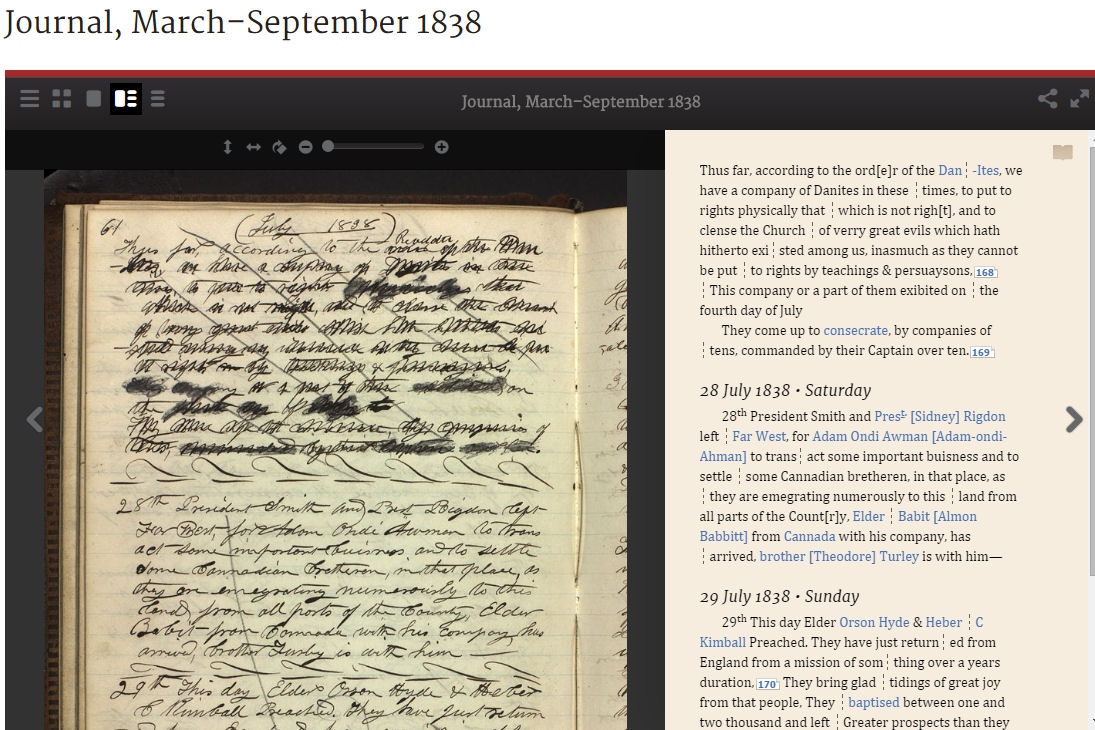
Did Joseph write in his private journal that he was aware of the Danite's purpose? Were these words then crossed out so that they wouldn't appear in the history of the Church?
27 July 1838 Friday
July 27th some time past the bretheren or saints have come up day after day to consecrate, and to bring their offerings into the store house of the lord, to prove him now herewith and se[e] if he will not pour us out a blessings that there will not be room enough to contain it,167 They have come up hither Thus far, according to the ord[e]r of the Dan-Ites, we have a company of Danites in these times, to put to rights physically that which is not righ[t], and to clense the Church of verry great evils which hath hitherto existed among us, inasmuch as they cannot be put to rights by teachings & persuaysons,168 This company or a part of them exibited on the fourth day of July They come up to consecrate, by companies of tens, commanded by their Captain over ten.[4]
See also Leland Gentry, The Danite Band of 1838, BYU Studies 14/4 (1974): 421—50.
Author's quote: "The Missourians actually seemed committed to continuing their pursuit of a peaceful co-existence with the Mormons."
Author's sources:
- Author's opinion.
Did Latter-day Saints plan to "take over" by voting?
Author's sources:
- Author's opinion.
Author's quote: "...calling their attention to the fact that the Saints were 'horse thieves, liars, counterfeiters, and dupes.'"
Author's sources:
- LeSueur, 61.
According to the author, after driving the Saints from their homes, Bogart started to threaten the Saints "in their own territory."
Author's sources:
- Author's statement.
Author's quote: "...the evidence clearly revealed that Joseph had directed most, if not all, of the illegal activities in which the Saints had been engaged."
Author's sources:
- Author's opinion.

FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
We are a volunteer organization. We invite you to give back.
Donate Now